Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
About Kafbat UI (UI for Apache Kafka)
Kafbat UI is a versatile, fast, lightweight, and flexible web interface designed to monitor and manage Apache Kafka® clusters. Created by developers for developers, it offers an intuitive way to gain visibility into your data flows, quickly identify and resolve issues, and maintain peak performance.
Kafbat UI is completely free and open source.
The streamlined dashboard provides clear insights into vital Kafka metrics—Brokers, Topics, Partitions, Production, and Consumption—making it easier to keep your systems running smoothly.
Developed by Kafbat, the team includes original contributors to the Apache Kafka UI project, continuing its legacy with a renewed vision. We're committed to evolving the project while staying true to its roots. Special thanks to Provectus for their foundational work, which remains a pillar of our progress and innovation.
Topic Insights – View essential topic details including partition count, replication status, and custom configurations.
Configuration Wizard – Set up and configure your Kafka clusters directly through the UI.
Multi-Cluster Management – Monitor and manage all your Kafka clusters in one unified interface.
Metrics Dashboard – Track key Kafka metrics in real time with a streamlined, lightweight dashboard.
Kafka Brokers Overview – Inspect brokers, including partition assignments and controller status.
Consumer Group Details – Analyze parked offsets per partition, and monitor both combined and partition-specific lag.
Message Browser – Explore messages in JSON, plain text, or Avro encoding formats. Live view is supported, enriched with user-defined CEL message filters.
Dynamic Topic Management – Create and configure new topics with flexible, real-time settings.
Pluggable Authentication – Secure your UI using OAuth 2.0 (GitHub, GitLab, Google), LDAP, or basic authentication.
Cloud IAM Support – Integrate with GCP IAM, Azure IAM, and AWS IAM for cloud-native identity and access management.
Managed Kafka Service Support – Full support for Azure EventHub, Google Cloud Managed Service for Apache Kafka, and AWS Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (MSK)—both server-based and serverless.
Custom SerDe Plugin Support – Use built-in serializers/deserializers like AWS Glue and Smile, or create your own custom plugins.
Role-Based Access Control – with RBAC.
Data Masking – in topic messages to enhance privacy and compliance.
MCP Server - Server
Kafbat UI is also available as a helm chart. See the underlying articles to learn more about it.
TODO :)
List of authentication methods to kafka itself
ACLs required to run the app
This list is enough to run the app in r/o mode
Permission | Operation | ResourceType | ResourceName | PatternType
------------+------------------+--------------+---------------+--------------
ALLOW | READ | TOPIC | * | LITERAL
ALLOW | DESCRIBE_CONFIGS | TOPIC | * | LITERAL
ALLOW | DESCRIBE | GROUP | * | LITERAL
ALLOW | DESCRIBE | CLUSTER | kafka-cluster | LITERAL
ALLOW | DESCRIBE_CONFIGS | CLUSTER | kafka-cluster | LITERALQuick start (demo run)
Ensure you have docker installed
Ensure your kafka cluster is available from the machine you're planning to run the app on
Run the following:
docker run -it -p 8080:8080 -e DYNAMIC_CONFIG_ENABLED=true ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-uiGo to `` and configure your first cluster by pressing on "Configure new cluster" button.
When you're done with testing, you can refer to the next articles to persist your config & deploy the app wherever you need to.
Kafbat-UI Project Roadmap
Roadmap exists in a form of a GitHub project board and is located .
The roadmap provides a list of features we decided to prioritize in project development. It should serve as a reference point to understand projects' goals.
We do prioritize them based on the feedback from the community, our own vision, and other conditions and circumstances.
The roadmap sets the general way of development. The roadmap is mostly about long-term features. All the features could be re-prioritized, rescheduled, or canceled.
Please ensure the target volume (~/kui/config.yml) of your config file does exist. If it doesn't, docker will create it as a directory instead of a file, and everything will explode.
Create a YAML file with the following contents:
Run the compose via:
Basic username+password authentication
Basic authentication supports only one local user. If you need multiple, running a Keycloak instance is the easiest way.
To enable basic username+password authentication, add these properties:
YAML config counterpart:
Please note that basic auth is incompatible with any other auth method or RBAC.
if you're running more than one pod and have authentication enabled you will encounter issues with sessions, as we store them in cookies and other instances are not aware of your sessions.
The solution for this would be using sticky session/session affinity.
An example:
To install the app via Helm please refer to .
If you're running AD rather than LDAP, also add these:
X, that doesn't mean we're not going to implement it. Feel free to raise the issue for consideration.
If a feature you want to see live is not present on the roadmap, but there's an issue with the feature, feel free to vote for it using reactions to the issue.Since the roadmap consists mostly of big long-term features, implementing them might be not easy for a beginner outside collaborator.
A good starting point is checking the contributing article.
These SerDes are developed and maintained by third parties; kafbat doesn't provide any support or warranties for these SerDes.

A list of ready-to-go docker compose files for various setup scenarios
Check our basic config examples: DOCKER_COMPOSE.MD
And our repo with more advanced examples: https://github.com/kafbat/ui-config-examples
services:
kafbat-ui:
container_name: kafbat-ui
image: ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui
ports:
- 8080:8080
environment:
DYNAMIC_CONFIG_ENABLED: true
volumes:
- ~/kui/config.yml:/etc/kafkaui/dynamic_config.yamldocker-compose -f <your-file>.yml up -d AUTH_TYPE: "LOGIN_FORM"
SPRING_SECURITY_USER_NAME: admin
SPRING_SECURITY_USER_PASSWORD: passauth:
type: LOGIN_FORM
spring:
security:
user:
name: admin
password: pass nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/affinity: cookie
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/affinity-mode: balanced
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/session-cookie-expires: "172800"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/session-cookie-max-age: "172800"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/session-cookie-name: kafbat-uiauth:
type: LDAP
spring:
ldap:
urls: ldap://localhost:10389
base: "cn={0},ou=people,dc=planetexpress,dc=com"
admin-user: "cn=admin,dc=planetexpress,dc=com"
admin-password: "GoodNewsEveryone"
user-filter-search-base: "dc=planetexpress,dc=com"
user-filter-search-filter: "(&(uid={0})(objectClass=inetOrgPerson))"
group-filter-search-base: "ou=people,dc=planetexpress,dc=com" # required for RBACoauth2:
ldap:
activeDirectory: true
domain: memelord.lolSet your git credentials:
git config --global user.name "Mona Lisa"
git config --global user.email "[email protected]"More info on setting git credentials:
To connect to Kafbat UI:
Open the http://127.0.0.1:8080 in the browser to access Kafbat UI
helm repo add kafka-ui https://kafbat.github.io/helm-charts
helm install kafka-ui kafka-ui/kafka-ui --set envs.config.KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME=local --set envs.config.KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS=kafka:9092kubectl port-forward svc/kafbat-ui 8080:80Build & Run Without Docker
Once you installed the prerequisites and cloned the repository, run the following steps in your project directory:
Execute the jar
java -Dspring.config.additional-location=<path-to-application-local.yml> --add-opens java.rmi/javax.rmi.ssl=ALL-UNNAMED -jar <path-to-kafbat-ui-jar>Example of how to configure clusters in the configuration file.
NOTE: If you want to get kafbat-ui up and running locally quickly without building the jar file manually, then just follow Running Without Docker Quickly
Proceed with building instructions from [[with-docker]] and disable/remove build-docker-images flag.
Command to build the jar
Once your build is successful and the jar file named kafbat-ui-api-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar is generated inside
kafbat-ui-api/target.
Execute the jar
Kafbat-UI allows you to log all operations to your kafka clusters done within kafbat-ui itself.
Logging can be done to either kafka topic and/or console.
See all the available configuration properties:
If you create the audit topic manually, it should not be compacted, as the audit documents do not have a key, which is required for Kafka topic compaction.
Other than compaction, the Kafka UI does not expect specific requirements for additional topic properties. However, as always, consider configuring the following:
Serialization, deserialization and custom plugins
Kafka-ui supports multiple ways to serialize/deserialize data.
You can specify a preferred serde for the topics key/value. This serde will be chosen by default in UI on topic's view/produce pages. To do so, set topicValuesPattern/topicValuesPattern properties for the selected serde. Kafka-ui will choose the first serde that matches the specified pattern.
Kafka-ui has integration with the (ODD).
ODD Platform allows you to monitor and navigate kafka data streams and see how they embed into your data platform.
This integration allows you to use kafbat-ui as an ODD "Collector" for kafka clusters.
Currently, kafbat-ui exports:
kafka topics as ODD Datasets with topic's metadata, configs, and schemas
Configuration properties:
INTEGATION_ODD_URL
integration.odd.ulr
ODD platform instance URL. Required.
INTEGRATION_ODD_TOKEN
integration.odd.token
Collector's token generated in ODD. Required.
INTEGRATION_ODD_TOPICSREGEX
integration.odd.topicsRegex
RegEx for topic names that should be exported to ODD. Optional, all topics exported by default.
Authentication methods for authenticating your users into the UI itself
Retention period How long the data should be stored in Kafka.
Number of partitions This affects parallelism and how the data will be consumed.
kafka:
clusters:
- name: local
audit:
topic-audit-enabled: true
console-audit-enabled: true
topic: '__kui-audit-log' # default name
audit-topic-properties: # any kafka topic properties in format of a map
retention.ms: 43200000
audit-topics-partitions: 1 # how many partitions, default is 1
level: all # either ALL or ALTER_ONLY (default). ALL will log all read operations.Build a docker image with the app
A successful build should produce a docker image named ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui with whatever version you've supplied.
Using Docker Compose
Start the app using docker image built in step 1 along with Kafka clusters:
Using Spring Boot Run
If you want to start only kafka clusters (to run the kafbat-ui app via spring-boot:run):
Then start the app.
Running in kubernetes
Using Helm Charts
To read more please follow to chart documentation.
To see the app running, navigate to http://localhost:8080.
Sample configuration:
You can specify which serde will be chosen in UI by default if no other serdes are selected via topicKeysPattern/topicValuesPattern settings.
Sample configuration:
If selected serde couldn't be applied (exception was thrown), then fallback (String serde with UTF-8 encoding) serde will be applied. Such messages will be specially highlighted in UI.
kafka:
clusters:
- name: Cluster1
serde:
- name: String
topicKeysPattern: click-events|imp-events
- name: Int64
topicKeysPattern: ".*-events"
- name: SchemaRegistry
topicValuesPattern: click-events|imp-eventsSee this example.
See this example.
Planned, see #478
We use CEL syntax for smart message filtersVariables bound to the context:
key (json if possible)
value (json if possible)
keyAsText
valueAsText
header
partition
timestampMs
JSON parsing logic:Key and Value (if parsing to JSON is available) are bound as JSON objects, otherwise as nulls.Filter examples:
has(record.keyAsText) && record.keyAsText.matches(".*[Gg]roovy.*") - regex for key as a string
has(record.key.name.first) && record.key.name.first == 'user1' - in case if the value is json
record.headers.size() == 1 && !has(record.headers.k1) && record.headers['k2'] == 'v2'
Sure! Swagger declaration is located here.
To create configmap use following command.\
If you have specified namespace use command.\
Encode secret with base64(You can use this tool https://www.base64encode.org/). Create secret.yaml file with the following content
If you have specified namespace for configmap and secret please use this command
kubectl create configmap ssl-files --from-file=kafka.truststore.jks --from-file=kafka.keystore.jksCreate values.yml file
Install by executing command
Create config map
This ConfigMap will be mounted to the Pod
Install by executing the command
Create config map
Install by executing the command
helm repo add kafbat-ui https://kafbat.github.io/helm-charts
helm install kafbat-ui kafbat-ui/kafka-uiImplement io.kafbat.ui.serde.api.Serde interface. See javadoc for implementation requirements.
Pack your serde into an uber jar, or provide a directory with no-dependency jar and its dependencies jars
Example pluggable serdes : kafka-smile-serde, kafka-glue-sr-serde
Sample configuration:
kafka:
clusters:
- name: Cluster1
serde:
- name: MyCustomSerde
className: my.lovely.org.KafkaUiSerde
filePath: /var/lib/kui-serde/my-kui-serde.jar
- name: MyCustomSerde2
className: my.lovely.org.KafkaUiSerde2
filePath: /var/lib/kui-serde2
properties:
prop1: v1Add the MCP server to your settings:
Open the co-pilot chat window and switch to agent mode.
Claude supports remote MCP servers only with an Enterprise subscription. For basic usage, configure a mcp-remote proxy:
"mcp": {
"servers": {
"Kafka UI": {
"type": "sse",
"url": "http://hostname:8080/mcp/sse"
}
}
}{
"mcpServers": {
"kafka": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-remote",
"http://localhost:8080/mcp/sse",
"--transport sse-only",
"--allow-http"
]
}
}
}./gradlew clean build \
# -x skips goals, in this cases tests. Tests take time, run them separately if needed.
-x test \
# building an app without frontend part could be useful for developing frontend or for using the app like an API client
-Pinclude-frontend=true \
# skip building a docker image if you only need a jar
-Pbuild-docker-images=true \
# version will be displayed in UI and used for tagging docker image. You can remove it.
-Pversion=<version>docker-compose -f ./.dev/dev.yaml up -ddocker-compose -f ./documentation/compose/kafka-clusters-only.yaml up -d./gradlew bootRun -x test
# or
./gradlew bootRun -x test -Dspring.config.location=file:///path/to/conf.yamlhelm repo add kafbat https://ui.charts.kafbat.io
helm install kafbat-ui kafbat/kafka-uikafka:
clusters:
- name: Cluster1
defaultKeySerde: Int32
defaultValueSerde: String
serde:
- name: Int32
topicKeysPattern: click-events|imp-eventsserver:
ssl:
trust-store: classpath:keycloak-truststore.jks
trust-store-password: changeitkubectl create configmap ssl-files --from-file=kafka.truststore.jks --from-file=kafka.keystore.jks -n {{namespace}apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: ssl-secret
# Specify namespace if needed, uncomment next line and provide namespace
#namespace: {namespace}
type: Opaque
data:
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD: ##Base 64 encoded secret
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SSL_KEYSTORE_PASSWORD: ##Base 64 encoded secretexistingSecret: "ssl-secret"
env:
- name: KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION
value: /ssl/kafka.truststore.jks
- name: KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SSL_KEYSTORE_LOCATION
value: /ssl/kafka.keystore.jks
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /ssl
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: ssl-fileshelm install kafbat-ui kafbat-ui/helm-charts -f ssl-values.yamlhelm install kafbat-ui kafbat-ui/helm-charts -f ssl-values.yaml -n {namespace}yamlApplicationConfig:
kafka:
clusters:
- name: yaml
bootstrapServers: kafka-cluster-broker-endpoints:9092
auth:
type: disabled
management:
health:
ldap:
enabled: falsehelm install kafbat-ui kafbat-ui/kafka-ui -f values.ymlapiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kafbat-ui-configmap
data:
config.yml: |-
kafka:
clusters:
- name: yaml
bootstrapServers: kafka-cluster-broker-endpoints:9092
auth:
type: disabled
management:
health:
ldap:
enabled: falsehelm install kafbat-ui kafbat-ui/kafka-ui --set yamlApplicationConfigConfigMap.name="kafbat-ui-configmap",yamlApplicationConfigConfigMap.keyName="config.yml"apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kafbat-ui-helm-values
data:
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: "kafka-cluster-name"
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: "kafka-cluster-broker-endpoints:9092"
AUTH_TYPE: "DISABLED"
MANAGEMENT_HEALTH_LDAP_ENABLED: "FALSE" helm install kafbat-ui kafbat-ui/kafka-ui --set existingConfigMap="kafbat-ui-helm-values"How to configure SASL SCRAM Authentication
By default, kafbat-ui does not allow to change of its configuration in runtime. When the application is started it reads configuration from system env, config files (ex. application.yaml), and JVM arguments (set by -D). Once the configuration was read it was treated as immutable and won't be refreshed even if the config source (ex. file) was changed.
Since version 0.6 we added an ability to change cluster configs in runtime. This option is disabled by default and should be implicitly enabled. To enable it, you should set DYNAMIC_CONFIG_ENABLED env property to true or add dynamic.config.enabled: true property to your yaml config file.
Sample docker compose configuration:
You can even omit all vars other than DYNAMIC_CONFIG_ENABLED to start the application with empty configs and setup it up after startup.
When the dynamic config feature is enabled you will see additional buttons that will take you to "Wizard" for editing existing cluster configuration or adding new clusters:
Kafbat-UI is a stateless application by its nature, so, when you edit configuration during runtime, it will store configuration additions on the container's filesystem (in dynamic_config.yaml file). Dynamic config file will be overridden on each configuration submission.
During the configuration process, you can also upload configuration-related files (like truststore and keystores). They will be stored in etc/kafkaui/uploads a folder with a unique timestamp suffix to prevent name collision. In the wizard, you can also use files that were mounted to the container's filesystem, without uploading them directly.
Note, that if the container is recreated, your edited (and uploaded) files won't be present and the app will be started with static configuration only. If you want to be able to keep the configuration created by wizard, you have to mount/copy the same files into newly created kafbat-ui containers (whole /etc/kafkaui/ folder, by default).
Properties, specified where dynamic config files will be persisted:
Currently, the new configuration submission leads to a full application restart. So, if your kafbat-ui app is starting slow (not a usual case, but may happen when you have a slow connection to kafka clusters) you may notice UI inaccessibility during restart time.
We as members, contributors, and leaders pledge to make participation in our community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body size, visible or invisible disability, ethnicity, sex characteristics, gender identity and expression, level of experience, education, socio-economic status, nationality, personal appearance, race, caste, color, religion, or sexual identity and orientation.
Login module control flag not specified in JAAS configIf you are running against confluent cloud and you have specified correctly the jass config and still continue getting these errors look to see if you are passing confluent. the license in the connector, the absence of a license returns a number of bogus errors like "Login module control flag not specified in JAAS config".
https://docs.confluent.io/platform/current/connect/license.html
A good resource for what properties are needed is here: https://gist.github.com/rmoff/49526672990f1b4f7935b62609f6f567
We pledge to act and interact in ways that contribute to an open, welcoming, diverse, inclusive, and healthy community.
Examples of behavior that contributes to a positive environment for our community include:
Demonstrating empathy and kindness toward other people
Being respectful of differing opinions, viewpoints, and experiences
Giving and gracefully accepting constructive feedback
Accepting responsibility and apologizing to those affected by our mistakes, and learning from the experience
Focusing on what is best not just for us as individuals, but for the overall community
Examples of unacceptable behavior include:
The use of sexualized language or imagery, and sexual attention or advances of any kind
Trolling, insulting or derogatory comments, and personal or political attacks
Public or private harassment
Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or email address, without their explicit permission
Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a professional setting
Community leaders are responsible for clarifying and enforcing our standards of acceptable behavior and will take appropriate and fair corrective action in response to any behavior that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive, or harmful.
Community leaders have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are not aligned to this Code of Conduct, and will communicate reasons for moderation decisions when appropriate.
This Code of Conduct applies within all community spaces, and also applies when an individual is officially representing the community in public spaces. Examples of representing our community include using an official e-mail address, posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed representative at an online or offline event.
Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be reported to the community leaders responsible for enforcement at email [email protected]. All complaints will be reviewed and investigated promptly and fairly.
All community leaders are obligated to respect the privacy and security of the reporter of any incident.
Community leaders will follow these Community Impact Guidelines in determining the consequences for any action they deem in violation of this Code of Conduct:
Community Impact: Use of inappropriate language or other behavior deemed unprofessional or unwelcome in the community.
Consequence: A private, written warning from community leaders, providing clarity around the nature of the violation and an explanation of why the behavior was inappropriate. A public apology may be requested.
Community Impact: A violation through a single incident or series of actions.
Consequence: A warning with consequences for continued behavior. No interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, for a specified period of time. This includes avoiding interactions in community spaces as well as external channels like social media. Violating these terms may lead to a temporary or permanent ban.
Community Impact: A serious violation of community standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior.
Consequence: A temporary ban from any sort of interaction or public communication with the community for a specified period of time. No public or private interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, is allowed during this period. Violating these terms may lead to a permanent ban.
Community Impact: Demonstrating a pattern of violation of community standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior, harassment of an individual, or aggression toward or disparagement of classes of individuals.
Consequence: A permanent ban from any sort of public interaction within the community.
This Code of Conduct is adapted from the Contributor Covenant, version 2.0, available at https://www.contributor-covenant.org/version/2/0/code_of_conduct.html.
Community Impact Guidelines were inspired by Mozilla's code of conduct enforcement ladder.
For answers to common questions about this code of conduct, see the FAQ at https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq. Translations are available at https://www.contributor-covenant.org/translations.
Check the required permissions.
https://github.com/provectus/kafka-ui/discussions/1104#discussioncomment-1656843 https://github.com/provectus/kafka-ui/discussions/1104#discussioncomment-2963449 https://github.com/provectus/kafka-ui/issues/2184#issuecomment-1198506124
Thanks to ahlooli#2666 on discord:
Create a secret in AWS secret manager store that contains key:value pair with 1 username and 1 password, there are certain rules to be followed like the name of the secret (eg. need to start with MSK_ **), so need to refer back to AWS documentation.
Proceed to MSK console and create the MSK cluster, my cluster was the "provisioned" type. Then choose SASL/SCRAM. Another option also needs to follow documentation for your preferred configuration.
After the Cluster has been created, you can then proceed to associate the Secrets created earlier to MSK cluster. (Done in MSK Console)
Then we can proceed to create a custom security group that allows port 9096 (or whichever MSK broker is using). Rough idea:
Source: ESK cluster security group
Type: TCP
Port: 9096
Find out all the MSK's broker ENI. Proceed to attach the above sec. group to each ENI. (if you have 3 brokers which means you have 3 Eni, you need to do it manually 1 by 1)
At this stage, the AWS side should have sufficient permission to allow kafbat-ui to communicate with it.
Increase webclient.max-in-memory-buffer-size property value. Default value is 20MB.
If you suffer from wrongfully generated redirect uris when behind a proxy/loadbalancer due to mismatch in public and origin ports/scheme.
Add the following property server.forward-headers-strategy=FRAMEWORK
You're running a new kafka version. Feel free to raise an issue for us to fix this, or raise a PR updating this file
docker run -p 8080:8080 \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME=<KAFKA_NAME> \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS=<KAFKA_URL> \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL=SASL_SSL \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_MECHANISM=SCRAM-SHA-512 \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_JAAS_CONFIG=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="<KAFKA_USERNAME>" password="<KAFKA_PASSWORD>"; \
-d ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui DYNAMIC_CONFIG_PATH
dynamic.config.path
/etc/kafkaui/dynamic_config.yaml
Path to dynamic config file
CONFIG_RELATED_UPLOADS_DIR
config.related.uploads.dir
/etc/kafkaui/uploads
Path where uploaded files will be placed


AWS profile-based authentication (awsProfileName)
IAM Role-based authentication (awsRoleArn with optional session config)
Please replace
<KAFKA_URL> with broker list
<PROFILE_NAME> with your AWS profile
<ROLE_ARN> with the AWS IAM Role ARN
<SESSION_NAME> with a custom role session name (optional)
<STS_REGION> with the AWS region for STS (optional)
Using awsProfileName:
Using awsRoleArn and optional fields:
Using awsProfileName:
Using awsRoleArn and optional fields:
version: '3.4'
services:
kafbat-ui:
image: ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui
container_name: kafbat-ui
ports:
- "888:8080"
restart: always
environment:
- KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME=<KAFKA_NAME>
- KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS=<KAFKA_URL>
- KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL=SASL_SSL
- KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_MECHANISM=SCRAM-SHA-512
- KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_JAAS_CONFIG=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="<KAFKA_USERNAME>" password="<KAFKA_PASSWORD>";
- KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_PROTOCOL=SASLkafka:
clusters:
- name: local
bootstrapServers: <KAFKA_URL>
properties:
security.protocol: SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism: SCRAM-SHA-512
sasl.jaas.config: org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="<KAFKA_USERNAME>" password="<KAFKA_PASSWORD>";services:
kafbat-ui:
container_name: kafbat-ui
image: ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui
ports:
- 8080:8080
depends_on:
- kafka0
environment:
DYNAMIC_CONFIG_ENABLED: 'true'
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: wizard_test
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: kafka0:29092
# ... docker run -p 8080:8080 \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME=local \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS=<KAFKA_URL> \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL=SASL_SSL \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_MECHANISM=AWS_MSK_IAM \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_CLIENT_CALLBACK_HANDLER_CLASS=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMClientCallbackHandler \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_JAAS_CONFIG='software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required awsProfileName="<PROFILE_NAME>";' \
-d ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui docker run -p 8080:8080 \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME=local \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS=<KAFKA_URL> \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL=SASL_SSL \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_MECHANISM=AWS_MSK_IAM \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_CLIENT_CALLBACK_HANDLER_CLASS=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMClientCallbackHandler \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_JAAS_CONFIG='software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required awsRoleArn="<ROLE_ARN>" awsRoleSessionName="<SESSION_NAME>" awsStsRegion="<STS_REGION>";' \
-d ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui kafka:
clusters:
- name: local
bootstrapServers: <KAFKA_URL>
properties:
security.protocol: SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism: AWS_MSK_IAM
sasl.client.callback.handler.class: software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMClientCallbackHandler
sasl.jaas.config: software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required awsProfileName="<PROFILE_NAME>";kafka:
clusters:
- name: local
bootstrapServers: <KAFKA_URL>
properties:
security.protocol: SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism: AWS_MSK_IAM
sasl.client.callback.handler.class: software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMClientCallbackHandler
sasl.jaas.config: software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required awsRoleArn="<ROLE_ARN>" awsRoleSessionName="<SESSION_NAME>" awsStsRegion="<STS_REGION>";This guide aims to walk you through the process of working on issues and Pull Requests (PRs).
Bear in mind that you will not be able to complete some steps on your own if you do not have “write” permission. Feel free to reach out to the maintainers to help you unlock these activities.
Please note that we have a code of conduct. Make sure that you follow it in all of your interactions with the project.
There are two options to look for the issues to contribute to. The first is our board. There the issues are sorted by the required experience level (beginner, intermediate, expert).
The second option is to search for -labeled issues. Some of them might not be displayed on the aforementioned board or vice versa.
You also need to consider labels. You can sort the issues by scope labels, such as scope/backend, scope/frontend or even scope/k8s. If any issue covers several specific areas, and you do not have the required expertise for one of them, just do your part of the work — others will do the rest.
There is a bunch of criteria that make an issue feasible for development. The implementation of any features and/or their enhancements should be reasonable and must be backed by justified requirements (demanded by the community, roadmap plans, etc.). The final decision is left to the maintainers' discretion.
All bugs should be confirmed as such (i.e. the behavior is unintended).
Any issue should be properly triaged by the maintainers beforehand, which includes:
Having a proper milestone set
Having required labels assigned: "accepted" label, scope labels, etc.
Formally, if these triage conditions are met, you can start to work on the issue.
With all these requirements met, feel free to pick the issue you want. Reach out to the maintainers if you have any questions.
Every issue “in progress” needs to be assigned to a corresponding person. To keep the status of the issue clear to everyone, please keep the card's status updated ("project" card to the right of the issue should match the milestone’s name).
Please refer to this guide.
In order to keep branch names uniform and easy to understand, please use the following conventions for branch naming.
Generally speaking, it is a good idea to add a group/type prefix to a branch; e.g., if you are working on a specific branch, you could name it issues/xxx.
Here is a list of good examples:
issues/123
feature/feature_name
bugfix/fix_thing\
Java: There is a file called checkstyle.xml in project root under etc directory.
You can import it into IntelliJ IDEA via Checkstyle plugin.
REST paths should be written in lowercase and consist of plural nouns only.
Also, multiple words that are placed in a single path segment should be divided by a hyphen (-).\
Query variable names should be formatted in camelCase.
Model names should consist of plural nouns only and should be formatted in camelCase as well.
When creating a PR please do the following:
In commit messages use these .
Link an issue(-s) via "linked issues" block.
Set the PR labels. Ensure that you set only the same set of labels that is present in the issue, and ignore yellow status/ labels.
When composing a build, ensure that any install or build dependencies have been removed before the end of the layer.
Update the README.md with the details of changes made to the interface. This includes new environment variables, exposed ports, useful file locations, and container parameters.
WIP
WIP
This guide has been written for MSK Serverless but is applicable for MSK in general as well.
Example ECS service configuration:
Go to the MSK page
Click "create cluster"
Choose "Custom create"
Choose "Serverless"
Go to IAM policies
Click "create policy"
Click "JSON"
Paste the following policy example in the editor, and replace "MSK ARN" with the ARN of your MSK cluster
Go to IAM
Click "Create role"
Choose AWS Services and EC2
On the next page find the policy which has been created in the previous step
Go to EC2
Choose your EC2 with Kafbat-UI
Go to Actions -> Security -> Modify IAM role
Choose the IAM role from previous step
The list of supported auth providers for RBAC
Any OAuth provider not on the list of all providers below this one.
Set up the auth itself first, docs here and here. Don't forget "custom-params.type: oauth".
Set up google auth
Set up github auth
Set up cognito auth
Set up AzureAD OAUTH2 auth
Set up LDAP auth
You can map Okta Groups to roles. First, confirm that your okta administrator has included the group claim or the groups will not be passed in the auth token.
Ensure roles-field in the auth config is set to groups and that groups is included in the scope, see for more details.
Configure the role mapping to the okta group via generic provider mentioned above:
You can map GoAuthentic Groups to roles. First, confirm that your GoAuthentic administrator has included the profile claim or the groups will not be passed in the auth token.
Ensure roles-field in the auth config is set to groups and that profile is included in the scope, as groups are passed by default in the profile scope. See for more details.
Configure the role mapping to the GoAuthentic group via generic provider mentioned above:
SerDes included in a default distribution
Big-endian 4/8 bytes representation of signed/unsigned integers.
Base64 (RFC4648) binary data representation. It can be useful in cases where the actual data is not important, but the same (byte-wise) key/value should be sent.
binary data representation. The byte delimiter and case can be configured.
Class name: io.kafbat.ui.serdes.builtin.HexSerde
Treats binary data as a string in the specified encoding. Default encoding is UTF-8.
Class name: io.kafbat.ui.serdes.builtin.StringSerde
Sample configuration (if you want to overwrite the default configuration):
Class name: io.kafbat.ui.serdes.builtin.ProtobufFileSerde
Sample configuration:
Deserialize-only serde. Decodes protobuf payload without a predefined schema (like protoc --decode_raw command).
SchemaRegistry serde is automatically configured if schema registry properties are set on the cluster level. But you can add new SchemaRegistry-typed serdes that will connect to another schema-registry instance.
Class name: io.kafbat.ui.serdes.builtin.sr.SchemaRegistrySerde
Sample configuration:
Deprecated. See OAuth2 guides
SSO require additionaly to configure TLS for application, in that example we will use self-signed certificate, in case of use legal certificates please skip step 1.
At this step we will generate self-signed PKCS12 keypair.
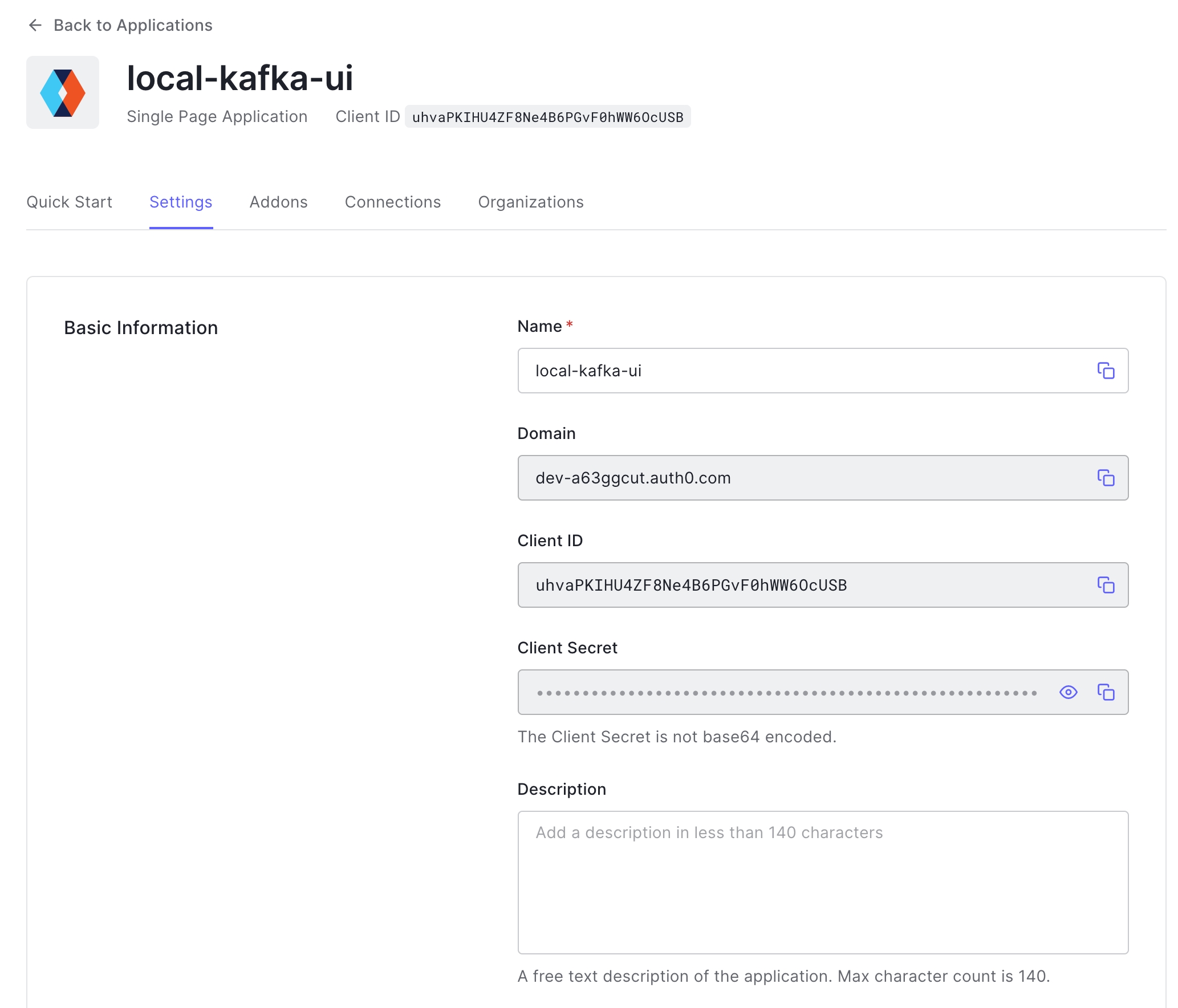
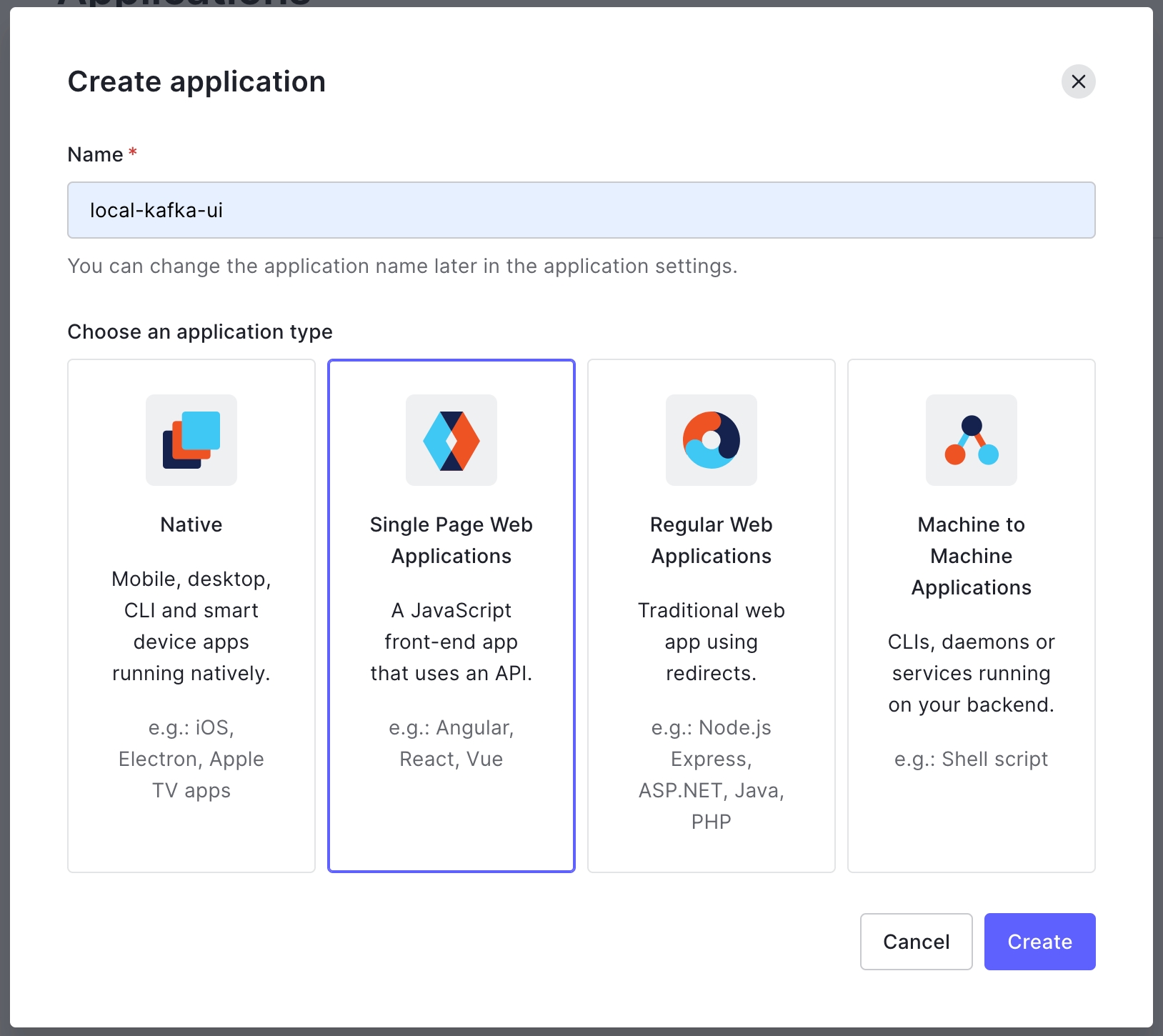
Create new application in any SSO provider, we will continue with .
After that need to provide callback URLs, in our case we will use https://127.0.0.1:8080/login/oauth2/code/auth0
This is a main parameters required for enabling SSO
To launch Kafbat UI with enabled TLS and SSO run following:
In the case with trusted CA-signed SSL certificate and SSL termination somewhere outside of application we can pass only SSO related environment variables:
If you're using load balancer/proxy and use HTTP between the proxy and the app, you might want to set server_forward-headers-strategy to native as well (SERVER_FORWARDHEADERSSTRATEGY=native), for more info refer to .
For Azure AD (Office365) OAUTH2 you'll want to add additional environment variables:
Note that scope is created by default when Application registration is done in Azure portal. You'll need to update application registration manifest to include "accessTokenAcceptedVersion": 2
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL=SASL_SSL
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_MECHANISM=AWS_MSK_IAM
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_JAAS_CONFIG='software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;'
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_CLIENT_CALLBACK_HANDLER_CLASS='software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMClientCallbackHandler'environment: [
{
name: "KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME",
value: config.mskClusterName
},
{
name: "KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS",
value: config.mskBootstrapServers
},
{
name: "KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_DISABLELOGDIRSCOLLECTION",
value: "true"
},
{
name: "KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL",
value: "SASL_SSL"
},
{
name: "KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_MECHANISM",
value: "AWS_MSK_IAM"
},
{
name: "KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_CLIENT_CALLBACK_HANDLER_CLASS",
value: "software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMClientCallbackHandler"
},
{
name: "KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SASL_JAAS_CONFIG",
value: "software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required awsDebugCreds=true;"
},
] subjects:
- provider: oauth
type: role
value: "role-name"
- provider: oauth
type: user
value: "zoidberg"Assign the PR to yourself. A PR assignee is someone whose goal is to get the PR merged.
Add reviewers. As a rule, reviewers' suggestions are pretty good; please use them.
Upon merging the PR, please use a meaningful commit message, the task name should be fine in this case.
Choose VPC and subnets
Choose the default security group or use the existing one
Click Update IAM role
git installed
docker installed
Note: For contributing, you must have a GitHub account to be able to raise PRs.
Install OpenJDK 25 package or newer:
Check the java version using the command java -version.
Note: In case OpenJDK 25 is not set as your default Java, run
to list all installed Java versions.
You can set it as the default by entering the selection number for it in the list and pressing Enter. For example, to set Java 25 as the default, you would enter 5 and press Enter.
Install git:
Install docker:
To execute the docker Command without sudo:
Install brew.
Install brew cask:
Install openjdk 25 via Homebrew:
Verify Installation
Note: In case OpenJDK 25 is not set as your default Java, you can consider including it in your $PATH after installation
If java_home doesn't recognize homebrew installed java you can run below cmd to symlink brew installed Java path to jvm
Consider allocating at least 4GB of memory for your docker. Otherwise, some apps within a stack (e.g. kafbat-ui.yaml) might crash.
To check how much memory is allocated to docker, use docker info.
You will find the total memory and used memory in the output. if you won't find used memory that means memory limits are not set for containers.
To allocate 4GB of memory for Docker:
MacOS
Edit docker daemon settings within docker dashboard
For Ubuntu
Open the Docker configuration file in a text editor using the following command:
Add the following line to the file to allocate 4GB of memory to Docker:
Save the file and exit the text editor.
Restart the Docker service using the following command:
Verify that the memory limit has been set correctly by running the following command:
Note that the warning messages are expected as they relate to the kernel not supporting cgroup memory limits.
Now any containers you run in docker will be limited to this amount of memory. You can also increase the memory limit as per your preference.
In the next section, you'll learn how to Build and Run kafbat-ui.
For json objects - remove target fields, otherwise - return "null" string.
Apply examples:
For json objects - replace target field's values with specified replacement string (by default with ***DATA_MASKED***). Note: if target field's value is object, then replacement applied to all its fields recursively (see example).
Apply examples:
Mask target field's values with specified masking characters, recursively (spaces and line separators will be kept as-is). maskingCharsReplacement array specifies what symbols will be used to replace upper-case chars (index 0), lower-case chars (index 1), digits (index 2) and other symbols (index 3) correspondingly.
Apply examples:
For each policy, if fields not specified, then policy will be applied to all object's fields or whole string if it is not a json-object.
You can specify which masks will be applied to topic's keys/values. Multiple policies will be applied if topic matches both policy's patterns.
Yaml configuration example:
Same configuration in env-vars fashion:
- type: REMOVE
fields: [ "id", "name" ]
...To set limits via CLI you need to specify limits with helm install command.
resources:
limits:
cpu: 200m
memory: 512Mi
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 256Mihelm install kafka-ui kafka-ui/kafka-ui -f values.yamlhelm install kafka-ui kafka-ui/kafka-ui --set resources.limits.cpu=200m --set resources.limits.memory=512Mi --set resources.requests.memory=256Mi --set resources.requests.cpu=200m {
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"kafka-cluster:Connect",
"kafka-cluster:DescribeCluster",
"kafka-cluster:AlterCluster",
"kafka-cluster:AlterClusterDynamicConfiguration",
"kafka-cluster:DescribeClusterDynamicConfiguration",
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:kafka:eu-central-1:297478128798:cluster/test-wizard/7b39802a-21ac-48fe-b6e8-a7baf2ae2533-s2"
},
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor1",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"kafka-cluster:ReadData",
"kafka-cluster:WriteData",
"kafka-cluster:DescribeTopicDynamicConfiguration",
"kafka-cluster:AlterTopicDynamicConfiguration",
"kafka-cluster:AlterTopic",
"kafka-cluster:CreateTopic",
"kafka-cluster:DescribeTopic",
"kafka-cluster:DeleteTopic"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:kafka:eu-central-1:297478128798:topic/test-wizard/7b39802a-21ac-48fe-b6e8-a7baf2ae2533-s2/*"
},
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor2",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"kafka-cluster:DeleteGroup",
"kafka-cluster:DescribeGroup",
"kafka-cluster:AlterGroup"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:kafka:eu-central-1:297478128798:group/test-wizard/7b39802a-21ac-48fe-b6e8-a7baf2ae2533-s2/*"
}
]
} - provider: oauth_google
type: domain
value: "memelord.lol"
- provider: oauth_google
type: user
value: "[email protected]" - provider: oauth_github
type: organization
value: "kafbat"
- provider: oauth_github
type: user
value: "memelord"
- provider: oauth_github
type: team
value: "kafbat/backend" - provider: oauth_cognito
type: user
value: "zoidberg"
- provider: oauth_cognito
type: group
value: "memelords" - provider: oauth
type: user
value: "[email protected]"
- provider: oauth
type: role
value: "admin" # From AzureAD Role Claims - provider: ldap
type: group
value: "admin_staff"
- provider: ldap
type: user
value: "pepega" - provider: ldap_ad
type: group
value: "admin_staff"
- provider: ldap_ad
type: user
value: "zoidberg" subjects:
- provider: oauth
type: role
value: "<okta-group-name>" subjects:
- provider: oauth
type: role
value: "<goauthentic-group-name>"kafka:
clusters:
- name: Cluster1
# Other Cluster configuration omitted ...
serde:
- name: HexWithEditedDelimiter
className: io.kafbat.ui.serdes.builtin.HexSerde
properties:
uppercase: "false"
delimiter: ":"kafka:
clusters:
- name: Cluster1
# Other Cluster configuration omitted ...
serde:
# registering String serde with custom config
- name: AsciiString
className: io.kafbat.ui.serdes.builtin.StringSerde
properties:
encoding: "ASCII"
# overriding build-it String serde config
- name: String
properties:
encoding: "UTF-16"kafka:
clusters:
- name: Cluster1
# Other Cluster configuration omitted ...
serde:
- name: ProtobufFile
properties:
# protobufFilesDir specifies root location for proto files (will be scanned recursively)
# NOTE: if 'protobufFilesDir' specified, then 'protobufFile' and 'protobufFiles' settings will be ignored
protobufFilesDir: "/path/to/my-protobufs"
# (DEPRECATED) protobufFile is the path to the protobuf schema. (deprecated: please use "protobufFiles")
protobufFile: path/to/my.proto
# (DEPRECATED) protobufFiles is the location of one or more protobuf schemas
protobufFiles:
- /path/to/my-protobufs/my.proto
- /path/to/my-protobufs/another.proto
# protobufMessageName is the default protobuf type that is used to deserialize
# the message's VALUE if the topic is not found in protobufMessageNameByTopic.
# optional, if not set, the first type in the file will be used as default
protobufMessageName: my.DefaultValType
# default protobuf type that is used for KEY serialization/deserialization
# optional
protobufMessageNameForKey: my.Type1
# mapping of topic names to protobuf types, that will be used for KEYS serialization/deserialization
# optional
protobufMessageNameForKeyByTopic:
topic1: my.KeyType1
topic2: my.KeyType2
# mapping of topic names to protobuf types, that will be used for VALUES serialization/deserialization
# optional
protobufMessageNameByTopic:
topic1: my.Type1
"topic.2": my.Type2kafka:
clusters:
- name: Cluster1
# this url will be used by "SchemaRegistry" by default
schemaRegistry: http://main-schema-registry:8081
serde:
- name: AnotherSchemaRegistry
className: io.kafbat.ui.serdes.builtin.sr.SchemaRegistrySerde
properties:
url: http://another-schema-registry:8081
# auth properties, optional
username: nameForAuth
password: P@ssW0RdForAuth
# and also add another SchemaRegistry serde
- name: ThirdSchemaRegistry
className: io.kafbat.ui.serdes.builtin.sr.SchemaRegistrySerde
properties:
url: http://another-yet-schema-registry:8081sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-25-jdkopenjdk 25.0.1 2025-10-21
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 25.0.1+8-27)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.0.1+8-27, mixed mode, sharing)sudo update-alternatives --config javaSelection Path Priority Status
------------------------------------------------------------
* 0 /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java 1111 auto mode
1 /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java 1111 manual mode
2 /usr/lib/jvm/java-16-openjdk-amd64/bin/java 1051 manual mode
3 /usr/lib/jvm/java-17-openjdk-amd64/bin/java 1021 manual mode
4 /usr/lib/jvm/java-21-openjdk-amd64/bin/java 1001 manual mode
5 /usr/lib/jvm/java-25-openjdk-amd64/bin/java 1001 manual mode
Press <enter> to keep the current choice[*], or type selection number:sudo apt install gitsudo apt update
sudo apt install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository -y "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu focal stable"
apt-cache policy docker-ce
sudo apt -y install docker-cesudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}
su - ${USER}
sudo chmod 666 /var/run/docker.sockbrew caskbrew install openjdk@25java -versionexport PATH="$(/usr/libexec/java_home -v 25)/bin:$PATH"
export JAVA_HOME="$(/usr/libexec/java_home -v 25)"sudo ln -sfn $(brew --prefix openjdk@21)/libexec/openjdk.jdk /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/openjdk-25.jdksudo nano /etc/default/dockerDOCKER_OPTS="--default-ulimit memlock=-1:-1 --memory=4g --memory-swap=-1"sudo service docker restartdocker info | grep -i memory{ "id": 1234, "name": { "first": "James" }, "age": 30 }
->
{ "age": 30 } non-json string -> null- type: REPLACE
fields: [ "id", "name" ]
replacement: "***" #optional, "***DATA_MASKED***" by default
...{ "id": 1234, "name": { "first": "James", "last": "Bond" }, "age": 30 }
->
{ "id": "***", "name": { "first": "***", "last": "***" }, "age": 30 } non-json string -> ***- type: MASK
fields: [ "id", "name" ]
maskingCharsReplacement: ["A", "a", "N", "_"] # optional, default is ["X", "x", "n", "-"]
...{ "id": 1234, "name": { "first": "James", "last": "Bond!" }, "age": 30 }
->
{ "id": "NNNN", "name": { "first": "Aaaaa", "last": "Aaaa_" }, "age": 30 } Some string! -> Aaaa aaaaaa_kafka:
clusters:
- name: ClusterName
# Other Cluster configuration omitted ...
masking:
- type: REMOVE
fields: [ "id" ]
topicKeysPattern: "events-with-ids-.*"
topicValuesPattern: "events-with-ids-.*"
- type: REPLACE
fields: [ "companyName", "organizationName" ]
replacement: "***MASKED_ORG_NAME***" #optional
topicValuesPattern: "org-events-.*"
- type: MASK
fields: [ "name", "surname" ]
maskingCharsReplacement: ["A", "a", "N", "_"] #optional
topicValuesPattern: "user-states"
- type: MASK
topicValuesPattern: "very-secured-topic"...
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_0_TYPE: REMOVE
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_0_FIELDS_0: "id"
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_0_TOPICKEYSPATTERN: "events-with-ids-.*"
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_0_TOPICVALUESPATTERN: "events-with-ids-.*"
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_1_TYPE: REPLACE
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_1_FIELDS_0: "companyName"
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_1_FIELDS_1: "organizationName"
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_1_REPLACEMENT: "***MASKED_ORG_NAME***"
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_1_TOPICVALUESPATTERN: "org-events-.*"
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_2_TYPE: MASK
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_2_FIELDS_0: "name"
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_2_FIELDS_1: "surname"
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_2_MASKING_CHARS_REPLACEMENT_0: 'A'
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_2_MASKING_CHARS_REPLACEMENT_1: 'a'
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_2_MASKING_CHARS_REPLACEMENT_2: 'N'
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_2_MASKING_CHARS_REPLACEMENT_3: '_'
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_2_TOPICVALUESPATTERN: "user-states"
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_3_TYPE: MASK
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_MASKING_3_TOPICVALUESPATTERN: "very-secured-topic"Configuration properties for all the things
A reminder: any of these properties can be converted into yaml config properties, an example:
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS
becomes
SERVER_SERVLET_CONTEXT_PATH
URI basePath
LOGGING_LEVEL_ROOT
Setting log level (trace, debug, info, warn, error). Default: info
How to Deploy Kafka UI from AWS Marketplace
Go to the AWS Marketplace website and sign in to your account.
Either use the search bar to find "Kafbat UI" or go to .
Click "Continue to Subscribe" and accept the terms and conditions. Click "Continue to Configuration".
Choose your desired software version and region. Click "Continue to Launch".
Choose "Launch from Website" and select your desired EC2 instance type. You can choose a free tier instance or choose a larger instance depending on your needs. We recommend having at least 512 RAM for an instant.
Next, select the VPC and subnet where you want the instance to be launched. If you don't have an existing VPC or subnet, you can create one by clicking "Create New VPC" or "Create New Subnet".
Choose your security group. A security group acts as a virtual firewall that controls traffic to and from your instance. If you don't have an existing security group, you can create a new one based on the seller settings by clicking "Create New Based on Seller Settings".
Give your security group a name and description. The seller settings will automatically populate the inbound and outbound rules for the security group based on best practices. You can review and modify the rules if necessary.
Click "Save" to create your new security group.
Select your key pair or create a new one. A key pair is used to securely connect to your instance via SSH. If you choose to create a new key pair, give it a name and click "Create". Your private key will be downloaded to your computer, so make sure to keep it in a safe place.
Finally, click "Launch" to deploy your instance. AWS will create the instance and install the Kafka UI software for you.
To check the EC2 state please click on "EC2 console".
After the instance is launched, you can check its status on the EC2 dashboard. Once it's running, you can access the Kafka UI by copying the public DNS name or IP address provided by AWS and adding after the IP address or DNS name port 8080.
Example: ec2-xx-xxx-x-xx.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com:8080
If your broker is deployed in AWS then allow incoming from Kafbat UI EC2 by adding an ingress rule in the security group which is used for a broker. If your broker is not in AWS then be sure that your broker can handle requests from Kafka-ui EC2 IP address.
More about permissions:
That's it! You've successfully deployed the Kafka UI from AWS Marketplace.
Kafka in kraft (zk-less) mode with multiple brokers
mkdir cert
keytool -genkeypair -alias ui-for-apache-kafka -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 \
-storetype PKCS12 -keystore cert/ui-for-apache-kafka.p12 -validity 3650docker run -p 8080:8080 -v `pwd`/cert:/opt/cert -e AUTH_TYPE=LOGIN_FORM \
-e SECURITY_BASIC_ENABLED=true \
-e SERVER_SSL_KEY_STORE_TYPE=PKCS12 \
-e SERVER_SSL_KEY_STORE=/opt/cert/ui-for-apache-kafka.p12 \
-e SERVER_SSL_KEY_STORE_PASSWORD=123456 \
-e SERVER_SSL_KEY_ALIAS=ui-for-apache-kafka \
-e SERVER_SSL_ENABLED=true \
-e SPRING_SECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_REGISTRATION_AUTH0_CLIENTID=uhvaPKIHU4ZF8Ne4B6PGvF0hWW6OcUSB \
-e SPRING_SECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_REGISTRATION_AUTH0_CLIENTSECRET=YXfRjmodifiedTujnkVr7zuW9ECCAK4TcnCio-i \
-e SPRING_SECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_PROVIDER_AUTH0_ISSUER_URI=https://dev-a63ggcut.auth0.com/ \
-e SPRING_SECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_REGISTRATION_AUTH0_SCOPE=openid \
-e TRUST_STORE=/opt/cert/ui-for-apache-kafka.p12 \
-e TRUST_STORE_PASSWORD=123456 \
ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-uidocker run -p 8080:8080 -v `pwd`/cert:/opt/cert -e AUTH_TYPE=OAUTH2 \
-e SPRING_SECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_REGISTRATION_AUTH0_CLIENTID=uhvaPKIHU4ZF8Ne4B6PGvF0hWW6OcUSB \
-e SPRING_SECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_REGISTRATION_AUTH0_CLIENTSECRET=YXfRjmodifiedTujnkVr7zuW9ECCAK4TcnCio-i \
-e SPRING_SECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_PROVIDER_AUTH0_ISSUER_URI=https://dev-a63ggcut.auth0.com/ \
-e SPRING_SECURITY_OAUTH2_CLIENT_REGISTRATION_AUTH0_SCOPE=openid \
ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-uidocker run -p 8080:8080 \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME="${cluster_name}"\
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS="${kafka_listeners}" \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_ZOOKEEPER="${zookeeper_servers}" \
-e KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECT_0_ADDRESS="${kafka_connect_servers}"
-e AUTH_TYPE=OAUTH2 \
-e AUTH_OAUTH2_CLIENT_AZURE_CLIENTID="xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx" \
-e AUTH_OAUTH2_CLIENT_AZURE_CLIENTSECRET="somesecret" \
-e AUTH_OAUTH2_CLIENT_AZURE_SCOPE="openid" \
-e AUTH_OAUTH2_CLIENT_AZURE_CLIENTNAME="azure" \
-e AUTH_OAUTH2_CLIENT_AZURE_PROVIDER="azure" \
-e AUTH_OAUTH2_CLIENT_AZURE_ISSUERURI="https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant_id}/v2.0" \
-e AUTH_OAUTH2_CLIENT_AZURE_JWKSETURI="https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant_id}/discovery/v2.0/keys" \
-d ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui"kafka:
clusters:
- bootstrapServers: xxxLOGGING_LEVEL_IO_KAFBAT_UI
Setting log level (trace, debug, info, warn, error). Default: debug
SERVER_PORT
Port for the embedded server. Default: 8080
KAFKA_ADMIN-CLIENT-TIMEOUT
Kafka API timeout in ms. Default: 30000
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME
Cluster name
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS
Address where to connect
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBSERVER
KSQL DB server address
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBSERVERAUTH_USERNAME
KSQL DB server's basic authentication username
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBSERVERAUTH_PASSWORD
KSQL DB server's basic authentication password
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBSERVERSSL_KEYSTORELOCATION
Path to the JKS keystore to communicate to KSQL DB
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBSERVERSSL_KEYSTOREPASSWORD
Password of the JKS keystore for KSQL DB
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES_SECURITY_PROTOCOL
Security protocol to connect to the brokers. For SSL connection use "SSL", for plaintext connection don't set this environment variable
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY
SchemaRegistry's address
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRYAUTH_USERNAME
SchemaRegistry's basic authentication username
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRYAUTH_PASSWORD
SchemaRegistry's basic authentication password
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRYSSL_KEYSTORELOCATION
Path to the JKS keystore to communicate to SchemaRegistry
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRYSSL_KEYSTOREPASSWORD
Password of the JKS keystore for SchemaRegistry
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_METRICS_SSL
Enable SSL for Metrics (for PROMETHEUS metrics type). Default: false.
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_METRICS_USERNAME
Username for Metrics authentication
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_METRICS_PASSWORD
Password for Metrics authentication
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_METRICS_KEYSTORELOCATION
Path to the JKS keystore to communicate to metrics source (JMX/PROMETHEUS). For advanced setup, see kafbat-ui-jmx-secured.yml
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_METRICS_KEYSTOREPASSWORD
Password of the JKS metrics keystore
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMANAMETEMPLATE
How keys are saved to schemaRegistry
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_METRICS_PORT
Open metrics port of a broker
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_METRICS_TYPE
Type of metrics retriever to use. Valid values are JMX (default) or PROMETHEUS. If Prometheus, then metrics are read from prometheus-jmx-exporter instead of jmx
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_READONLY
Enable read-only mode. Default: false
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECT_0_NAME
Given name for the Kafka Connect cluster
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECT_0_ADDRESS
Address of the Kafka Connect service endpoint
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECT_0_USERNAME
Kafka Connect cluster's basic authentication username
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECT_0_PASSWORD
Kafka Connect cluster's basic authentication password
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECT_0_KEYSTORELOCATION
Path to the JKS keystore to communicate to Kafka Connect
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECT_0_KEYSTOREPASSWORD
Password of the JKS keystore for Kafka Connect
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_POLLING_THROTTLE_RATE
Max traffic rate (bytes/sec) that kafbat-ui allowed to reach when polling messages from the cluster. Default: 0 (not limited)
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_SSL_TRUSTSTORELOCATION
Path to the JKS truststore to communicate to Kafka Connect, SchemaRegistry, KSQL, Metrics
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_SSL_TRUSTSTOREPASSWORD
Password of the JKS truststore for Kafka Connect, SchemaRegistry, KSQL, Metrics
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_SSL_VERIFYSSL
If set to false, SSL certificate of the host won't be verified. True by default.
KAFKA_CONFIG_SANITIZER_ENABLED
If set to false, disable configuration sanitizer (secret masking)
TOPIC_RECREATE_DELAY_SECONDS
Time delay between topic deletion and topic creation attempts for topic recreate functionality. Default: 1
TOPIC_RECREATE_MAXRETRIES
Number of attempts of topic creation after topic deletion for topic recreate functionality. Default: 15
DYNAMIC_CONFIG_ENABLED
Allow to change application config in runtime. Default: false.
kafka_internalTopicPrefix
Set a prefix for internal topics. Defaults to "_".
server.reactive.session.timeout
Session timeout. If a duration suffix is not specified, seconds will be used.
---
version: '2'
services:
kafbat-ui:
container_name: kafbat-ui
image: ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui
ports:
- 8080:8080
depends_on:
- kafka0
- kafka1
- kafka2
- schema-registry0
- kafka-connect0
environment:
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: local
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: kafka0:29092,kafka1:29092,kafka2:29092
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_METRICS_PORT: 9997
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY: http://schema-registry0:8085
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECT_0_NAME: first
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECT_0_ADDRESS: http://kafka-connect0:8083
kafka0:
image: confluentinc/cp-kafka:7.2.1
hostname: kafka0
container_name: kafka0
ports:
- 9092:9092
- 9997:9997
environment:
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: PLAINTEXT:PLAINTEXT,CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT,PLAINTEXT_HOST:PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: PLAINTEXT://kafka0:29092,PLAINTEXT_HOST://localhost:9092
KAFKA_INTER_BROKER_LISTENER_NAME: PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_OFFSETS_TOPIC_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_GROUP_INITIAL_REBALANCE_DELAY_MS: 0
KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_MIN_ISR: 1
KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_PROCESS_ROLES: 'broker,controller'
KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID:
KAFKA_NODE_ID: 1
KAFKA_CONTROLLER_QUORUM_VOTERS: '1@kafka0:29093,2@kafka1:29093,3@kafka2:29093'
KAFKA_LISTENERS: 'PLAINTEXT://kafka0:29092,CONTROLLER://kafka0:29093,PLAINTEXT_HOST://0.0.0.0:9092'
KAFKA_CONTROLLER_LISTENER_NAMES: 'CONTROLLER'
KAFKA_LOG_DIRS: '/tmp/kraft-combined-logs'
KAFKA_JMX_PORT: 9997
KAFKA_JMX_OPTS: -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=kafka0 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.rmi.port=9997
volumes:
- ./scripts/update_run_cluster.sh:/tmp/update_run.sh
- ./scripts/clusterID:/tmp/clusterID
command: "bash -c 'if [ ! -f /tmp/update_run.sh ]; then echo \"ERROR: Did you forget the update_run.sh file that came with this docker-compose.yml file?\" && exit 1 ; else /tmp/update_run.sh && /etc/confluent/docker/run ; fi'"
kafka1:
image: confluentinc/cp-kafka:7.2.1
hostname: kafka1
container_name: kafka1
environment:
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: PLAINTEXT:PLAINTEXT,CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT,PLAINTEXT_HOST:PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: PLAINTEXT://kafka1:29092,PLAINTEXT_HOST://localhost:9092
KAFKA_INTER_BROKER_LISTENER_NAME: PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_OFFSETS_TOPIC_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_GROUP_INITIAL_REBALANCE_DELAY_MS: 0
KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_MIN_ISR: 1
KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_PROCESS_ROLES: 'broker,controller'
KAFKA_NODE_ID: 2
KAFKA_CONTROLLER_QUORUM_VOTERS: '1@kafka0:29093,2@kafka1:29093,3@kafka2:29093'
KAFKA_LISTENERS: 'PLAINTEXT://kafka1:29092,CONTROLLER://kafka1:29093,PLAINTEXT_HOST://0.0.0.0:9092'
KAFKA_CONTROLLER_LISTENER_NAMES: 'CONTROLLER'
KAFKA_LOG_DIRS: '/tmp/kraft-combined-logs'
KAFKA_JMX_PORT: 9997
KAFKA_JMX_OPTS: -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=kafka1 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.rmi.port=9997
volumes:
- ./scripts/update_run_cluster.sh:/tmp/update_run.sh
- ./scripts/clusterID:/tmp/clusterID
command: "bash -c 'if [ ! -f /tmp/update_run.sh ]; then echo \"ERROR: Did you forget the update_run.sh file that came with this docker-compose.yml file?\" && exit 1 ; else /tmp/update_run.sh && /etc/confluent/docker/run ; fi'"
kafka2:
image: confluentinc/cp-kafka:7.2.1
hostname: kafka2
container_name: kafka2
environment:
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: PLAINTEXT:PLAINTEXT,CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT,PLAINTEXT_HOST:PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: PLAINTEXT://kafka2:29092,PLAINTEXT_HOST://localhost:9092
KAFKA_INTER_BROKER_LISTENER_NAME: PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_OFFSETS_TOPIC_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_GROUP_INITIAL_REBALANCE_DELAY_MS: 0
KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_MIN_ISR: 1
KAFKA_TRANSACTION_STATE_LOG_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
KAFKA_PROCESS_ROLES: 'broker,controller'
KAFKA_NODE_ID: 3
KAFKA_CONTROLLER_QUORUM_VOTERS: '1@kafka0:29093,2@kafka1:29093,3@kafka2:29093'
KAFKA_LISTENERS: 'PLAINTEXT://kafka2:29092,CONTROLLER://kafka2:29093,PLAINTEXT_HOST://0.0.0.0:9092'
KAFKA_CONTROLLER_LISTENER_NAMES: 'CONTROLLER'
KAFKA_LOG_DIRS: '/tmp/kraft-combined-logs'
KAFKA_JMX_PORT: 9997
KAFKA_JMX_OPTS: -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=kafka1 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.rmi.port=9997
volumes:
- ./scripts/update_run_cluster.sh:/tmp/update_run.sh
- ./scripts/clusterID:/tmp/clusterID
command: "bash -c 'if [ ! -f /tmp/update_run.sh ]; then echo \"ERROR: Did you forget the update_run.sh file that came with this docker-compose.yml file?\" && exit 1 ; else /tmp/update_run.sh && /etc/confluent/docker/run ; fi'"
schema-registry0:
image: confluentinc/cp-schema-registry:7.2.1
ports:
- 8085:8085
depends_on:
- kafka0
environment:
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_KAFKASTORE_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: PLAINTEXT://kafka0:29092
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_KAFKASTORE_SECURITY_PROTOCOL: PLAINTEXT
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_HOST_NAME: schema-registry0
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_LISTENERS: http://schema-registry0:8085
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_SCHEMA_REGISTRY_INTER_INSTANCE_PROTOCOL: "http"
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_LOG4J_ROOT_LOGLEVEL: INFO
SCHEMA_REGISTRY_KAFKASTORE_TOPIC: _schemas
kafka-connect0:
image: confluentinc/cp-kafka-connect:7.2.1
ports:
- 8083:8083
depends_on:
- kafka0
- schema-registry0
environment:
CONNECT_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: kafka0:29092
CONNECT_GROUP_ID: compose-connect-group
CONNECT_CONFIG_STORAGE_TOPIC: _connect_configs
CONNECT_CONFIG_STORAGE_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
CONNECT_OFFSET_STORAGE_TOPIC: _connect_offset
CONNECT_OFFSET_STORAGE_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
CONNECT_STATUS_STORAGE_TOPIC: _connect_status
CONNECT_STATUS_STORAGE_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1
CONNECT_KEY_CONVERTER: org.apache.kafka.connect.storage.StringConverter
CONNECT_KEY_CONVERTER_SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL: http://schema-registry0:8085
CONNECT_VALUE_CONVERTER: org.apache.kafka.connect.storage.StringConverter
CONNECT_VALUE_CONVERTER_SCHEMA_REGISTRY_URL: http://schema-registry0:8085
CONNECT_INTERNAL_KEY_CONVERTER: org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
CONNECT_INTERNAL_VALUE_CONVERTER: org.apache.kafka.connect.json.JsonConverter
CONNECT_REST_ADVERTISED_HOST_NAME: kafka-connect0
CONNECT_PLUGIN_PATH: "/usr/share/java,/usr/share/confluent-hub-components,/usr/share/filestream-connectors,/tmp/kfk"
volumes:
- /tmp/kfk:/tmp/kfk:ro
- /tmp/kfk/test.txt:/tmp/kfk/test.txt
kafka-init-topics:
image: confluentinc/cp-kafka:7.2.1
volumes:
- ./message.json:/data/message.json
depends_on:
- kafka0
command: "bash -c 'echo Waiting for Kafka to be ready... && \
cub kafka-ready -b kafka0:29092 1 30 && \
kafka-topics --create --topic second.users --partitions 3 --replication-factor 1 --if-not-exists --bootstrap-server kafka0:29092 && \
kafka-topics --create --topic second.messages --partitions 2 --replication-factor 1 --if-not-exists --bootstrap-server kafka0:29092 && \
kafka-topics --create --topic first.messages --partitions 2 --replication-factor 1 --if-not-exists --bootstrap-server kafka0:29092 && \
kafka-console-producer --bootstrap-server kafka0:29092 --topic second.users < /data/message.json'"
Examples of setups for different OAuth providers
In general, the structure of the Oauth2 config looks as follows:
For specific providers like Github (non-enterprise) and Google (), you don't have to specify URIs as they're well known.
Furthermore, other providers that support allow fetching URIs configuration from a /.well-known/openid-configuration endpoint. Depending on your setup, you may only have to set the issuer-uri of your provider to enable OIDC Service Discovery.
Example of callback URL for github OAuth app settings:
https://kafbat.io/login/oauth2/code/github
For the self-hosted installation find the properties a little bit below.
Replace HOSTNAME by your self-hosted platform FQDN.
This page explains configuration file structure
Let's start with that there are two possible ways to configure the app, they can interchange each other or even supplement each other.
There are two ways: YAML config & env. variables config. We strongly recommend using YAML in favor of env variables for the most part of the config. You can use env vars to override the default config on some different environments.
can help you to translate your config back and forth from YAML to env vars.
We will mostly provide examples of configs in YAML format, but sometimes single properties might be written in form of env variables.
Rather than writing your config from a scratch, it would be more convenient to use one of the ready-to-go and adjust it to your needs.
auth:
type: OAUTH2
oauth2:
client:
<unique_name>:
clientId: xxx
clientSecret: yyy
scope: openid
client-name: cognito # will be displayed on the login page
provider: <provider>
redirect-uri: http://localhost:8080/login/oauth2/code/<provider>
authorization-grant-type: authorization_code
issuer-uri: https://xxx
jwk-set-uri: https://yyy/.well-known/jwks.json
user-name-attribute: <zzz>
custom-params:
type: <provider_type> # fill this if you're gonna use RBAC. Supported values: cognito, google, github, oauth (for other generic providers)
roles-field: groups # required for RBAC, a field name in OAuth token which will contain user's roles/groupsDocker:
Docker compose:
Jar: java -Dspring.config.additional-location=<path-to-application-local.yml> -jar <path-to-jar>.jar
docker run -it \
-p 8080:8080 \
-e spring.config.additional-location=/tmp/config.yml \
-v /tmp/kui/config.yml:/tmp/config.yml \
ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-uiservices:
kafbat-ui:
container_name: kafbat-ui
image: ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui
environment:
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: local
# other properties, omitted
SPRING_CONFIG_ADDITIONAL-LOCATION: /config.yml
volumes:
- /tmp/config.yml:/config.ymlThere are two types of images we publish:
Release images, tagged with latest and simultaneously semver tags like v1.0.0
Snapshot images for every commit pushed to the main branch, named as the respective commit's short SHA, like b241abe. The latest build of the main branch is always tagged as main as well
Sometimes, for people who require recent changes that are not yet released, we suggest pulling snapshot images. These are usually safe to use, breaking changes happen rarely. To prevent pulling new versions, you can pin the version using the sha-named tag rather than main .
We publish our container images to these registries:
GHCR (Github Container Registry) — ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui:latest
AWS ECR (Elastic Container Registry) — public.ecr.aws/kafbat/kafka-ui:latest
Docker Hub — kafbat/kafka-ui:latest
GHCR is considered the main registry for various reasons, the rest are treated as mirrors. You can use these registries to avoid being ratioed by these services (GHCR requires authentication to pull images, Docker Hub is known to have pull limits).
GHCR contains all our images (release and snapshots), while the others store only release versions.
In the future, we will consider distributing snapshots to all the registries as a separate package.
Please refer to our configuration page to proceed with further app configuration.
Quick start with building
Liveliness and readiness endpoint is at /actuator/health.
Info endpoint (build info) is located at /actuator/info.
All of the environment variables/config properties could be found here.
Please refer to contributing guide, we'll guide you from there.
kafka:
clusters:
- name: local
bootstrapServers: localhost:9092
# ...
auth:
type: OAUTH2
oauth2:
client:
cognito:
clientId: xxx
clientSecret: yyy
scope: openid
client-name: cognito
provider: cognito
redirect-uri: http://localhost:8080/login/oauth2/code/cognito
authorization-grant-type: authorization_code
issuer-uri: https://cognito-idp.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/eu-central-1_xxx
jwk-set-uri: https://cognito-idp.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/eu-central-1_xxx/.well-known/jwks.json
user-name-attribute: cognito:username
custom-params:
type: cognito
logoutUrl: https://<XXX>>.eu-central-1.amazoncognito.com/logout #required just for cognitokafka:
clusters:
- name: local
bootstrapServers: localhost:9092
# ...
auth:
type: OAUTH2
oauth2:
client:
google:
provider: google
clientId: xxx.apps.googleusercontent.com
clientSecret: GOCSPX-xxx
user-name-attribute: email
custom-params:
type: google
allowedDomain: kafbat.io # for RBACkafka:
clusters:
- name: local
bootstrapServers: localhost:9092
# ...
auth:
type: OAUTH2
oauth2:
client:
azure:
clientId: "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
clientSecret: "somesecret"
scope: openid
client-name: azure
provider: azure
issuer-uri: "https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant_id}/v2.0"
jwk-set-uri: "https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant_id}/discovery/v2.0/keys"
user-name-attribute: email # Needed for RBAC roles matching
custom-params: # Needed for RBAC configuration
type: oauth
roles-field: roles # AzureAD Role Claims kafka:
clusters:
- name: local
bootstrapServers: localhost:9092
# ...
auth:
type: OAUTH2
oauth2:
client:
github:
provider: github
clientId: xxx
clientSecret: yyy
scope: read:org
user-name-attribute: login
custom-params:
type: githubkafka:
clusters:
- name: local
bootstrapServers: localhost:9092
# ...
auth:
type: OAUTH2
oauth2:
client:
github:
provider: github
clientId: xxx
clientSecret: yyy
scope: read:org
user-name-attribute: login
authorization-uri: http(s)://HOSTNAME/login/oauth/authorize
token-uri: http(s)://HOSTNAME/login/oauth/access_token
user-info-uri: http(s)://HOSTNAME/api/v3/user
custom-params:
type: github auth:
type: OAUTH2
oauth2:
client:
okta:
clientId: xxx
clientSecret: yyy
scope: [ 'openid', 'profile', 'email', 'groups' ] # default for okta + groups for rbac
client-name: Okta
provider: okta
redirect-uri: http://localhost:8080/login/oauth2/code/okta
authorization-grant-type: authorization_code
issuer-uri: https://<okta_domain>.okta.com
jwk-set-uri: https://yyy/.well-known/jwks.json
user-name-attribute: sub # default for okta, "email" also available
custom-params:
type: oauth
roles-field: groups # required for RBACauth:
type: OAUTH2
oauth2:
client:
keycloak:
clientId: xxx
clientSecret: yyy
scope: openid
issuer-uri: https://<keycloak_instance>/auth/realms/<realm>
user-name-attribute: preferred_username
client-name: keycloak
provider: keycloak
custom-params:
type: oauthauth:
type: OAUTH2
oauth2:
client:
goauthentic:
provider: goauthentic
clientId: xxx
clientSecret: yyy
scope: [ 'openid', 'profile', 'email' ]
client-name: goauthentic
issuer-uri: https://<goauthentic_instance>/application/o/<slug>/
user-name-attribute: nickname # OR "name", "given_name", "email", "preferred_username"
redirect-uri: http://localhost:8080/login/oauth2/code/goauthentic
authorization-grant-type: authorization_code
custom-params:
type: oauth
roles-field: groups
logoutUrl: https://<goauthentic_instance>/application/o/<slug>/end-session/# ======================================================
# Kafka Clusters Configuration
# Define all Kafka cluster-specific settings and related integrations.
# ======================================================
kafka:
clusters:
- name: local # Unique name identifier for the Kafka cluster
bootstrap-servers: kafka1:9092,kafka2:9092 # List of Kafka broker addresses
# SSL configuration for secure connection to Kafka brokers
ssl:
truststore-location: path/to/truststore/file.jks # Path to truststore JKS file
truststore-password: password # Password to access the truststore
verify-ssl: true # Enable SSL certificate verification
# Schema Registry connection and authentication details
schemaRegistry: http://schema-registry:8085
schema-registry-auth:
username: schema registry username
password: schema registry password
schema-registry-ssl:
keystore-location: path/to/keystore/file.jks
keystore-password: password
# ksqlDB connection and security settings
ksqldb-server: http://ksqldb-host:8088
ksqldb-server-auth:
username: ksqldb-username
password: ksqdb-passsword
ksqldb-server-ssl:
keystore-location: path/to/keystore/file.jks
keystore-password: password
# Kafka Connect REST endpoint and optional authentication
kafka-connect:
- name: first # Identifier for the Connect cluster
address: http://kafka-connect-host:8083
username: Auth username
password: Auth password
keystore-location: path/to/keystore/file.jks
keystore-password: keystore password
# Custom SerDe (Serializer/Deserializer) for interpreting topic data
serde:
- name: CustomeHexWithEditedDelimiter
class-name: io.kafbat.ui.serdes.builtin.HexSerde
file-path: /var/lib/kui-serde/my-kui-serde.jar
topic-keys-pattern: ".*-events" # Regex to match applicable topic keys
topic-values-pattern: ".*-events" # Regex to match applicable topic values
properties:
uppercase: "false" # Output lowercase hex
delimiter: ":" # Byte delimiter
default-key-serde: String # Default SerDe for message keys
default-value-serde: SchemaRegistry # Default SerDe for message values
# Monitoring and metrics collection from the cluster
metrics:
type: JMX # Available options: JMX or PROMETHEUS
port: 9997 # Port to collect JMX metrics
username: Auth username
password: Auth password
ssl: false # Whether to use SSL for metrics endpoint
keystore-location: path/to/keystore/file.jks
keystore-password: password
# Global Kafka client properties
properties:
"security.protocol": SASL_SSL
"sasl.mechanism": SCRAM-SHA-512
"sasl.jaas.config": org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="your-username" password="your-password";
# Kafka Consumer configuration overrides
consumer-properties:
"max.partition.fetch.bytes": 1048576
# Kafka Producer configuration overrides
producer-properties:
"enable.idempotence": false
read-only: true # Prevent write operations from the UI
polling-throttle-rate: 0 # Delay (seconds) between polling intervals in UI; 0 = no throttling
# Data masking rules for messages shown in the UI
masking:
- type: MASK # Action: MASK, REMOVE, or REPLACE
fields: [ "id", "name" ] # Specific fields to apply masking to
fields-name-pattern: "id.*" # Regex pattern to match field names
masking-chars-replacement: ["A", "a", "N", "_"] # Optional: override default mask characters
replacement: "***MASKED_FIELD_NAME***" # Replacement string for masked field names
topic-values-pattern: events-with-ids-.* # Apply on topic values matching this pattern
topic-keys-pattern: events-with-ids-.* # Apply on topic keys matching this pattern
# Audit logging configuration
audit:
topic-audit-enabled: false # Enable/disable Kafka topic audit logs
console-audit-enabled: false # Enable/disable console audit output
topic: audit-topic-name # Kafka topic for audit entries
audit-topics-partitions: 3 # Number of partitions for the audit topic
level: ALL # ALL = log all actions, ALTER_ONLY = only mutating actions
audit-topic-properties:
"retention.ms": 43200000 # Audit log retention in ms (12 hours)
# Prefix to identify internal Kafka topics used by system tools
internalTopicPrefix: "__"
# Timeout for admin Kafka operations (in milliseconds)
admin-client-timeout: 30000
# Polling behavior for consumer previews in the UI
polling:
poll-timeout-ms: 1000 # How long to wait for new records (ms)
max-page-size: 500 # Maximum number of records per poll
default-page-size: 100 # Default number of records per poll
# ======================================================
# Model Context Protocol config
# ======================================================
mcp:
enabled: true # Enable MCP (ModelContextProtocol) endpoint
# ======================================================
# OAuth2 Authentication Configuration
# Used for authenticating users via external identity providers.
# ======================================================
auth:
oauth2:
client:
client_name:
client-id: xxx
client-secret: yyy
scope: openid
client-name: cognito # Display name on the login screen
provider: <provider> # Path alias used in redirect URI
redirect-uri: http://localhost:8080/login/oauth2/code/<provider>
authorization-grant-type: authorization_code
issuer-uri: https://xxx # Identity provider URL
jwk-set-uri: https://yyy/.well-known/jwks.json # Public key set URL
user-name-attribute: <zzz> # JWT field used as the user's name
custom-params:
type: <provider_type> # Optional RBAC integration type (e.g. cognito, google, github, oauth)
roles-field: groups # Field containing user roles/groups
resource-server:
jwt:
jwk-set-uri: http://jwk/uri
jws-algorithms: ["RS256"]
issuer-uri: http://issuer/uri
public-key-location: # Optional path to JWT public key
audiences: [] # List of accepted audience values in JWT
authority_prefix: # Optional prefix added to authorities
authorities-claim-delimiter: # Regex delimiter for splitting roles
authorities-claim-name: # Claim name holding roles/permissions
principal-claim-name: # Claim used for determining the username
opaque-token:
client-id: # Client ID used for introspection
client-secret: # Secret used for introspection
introspection-uri: # URL to the introspection endpoint
# ======================================================
# LDAP Configuration
# Used for user and group resolution in RBAC when using LDAP.
# ======================================================
spring:
ldap:
urls: ldap://localhost:10389
base: "cn={0},ou=people,dc=planetexpress,dc=com"
admin-user: "cn=admin,dc=planetexpress,dc=com"
admin-password: "GoodNewsEveryone"
user-filter-search-base: "dc=planetexpress,dc=com"
user-filter-search-filter: "(&(uid={0})(objectClass=inetOrgPerson))"
group-filter-search-base: "ou=people,dc=planetexpress,dc=com"
# ======================================================
# Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
# Configure roles, user/group bindings, and permissions.
# ======================================================
rbac:
roles:
- name: "memelords" # Role name
clusters:
- local # Clusters this role applies to
subjects:
- provider: oauth_google # e.g. oauth_{client_name}, ldap
type: domain # domain, organization, user, group
value: "kafbat.dev"
regex: false
permissions:
- resource: applicationconfig # Resource types: applicationconfig, clusterconfig, topic, consumer, schema, connect, ksql, acl, audit
value: ".*"
actions: all # Allowed actions: read, write, all
# ======================================================
# WebClient Settings
# Configuration for HTTP clients used by the app.
# ======================================================
webclient:
response-timeout-ms: 20000 # Timeout for all outgoing HTTP requests
max-in-memory-buffer-size: 20MB # Maximum buffer size for handling responses
# ======================================================
# Spring Boot Actuator
# Enables health, info, and Prometheus endpoints for monitoring.
# ======================================================
management:
endpoint:
info:
enabled: true
health:
enabled: true
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "info,health,prometheus"
# ======================================================
# Application Logging Configuration
# Configure logging levels for specific packages.
# ======================================================
logging:
level:
root: INFO
io.kafbat.ui: DEBUG
reactor.netty.http.server.AccessLog: INFO
org.hibernate.validator: WARN
docker run -it -p 8080:8080 -e DYNAMIC_CONFIG_ENABLED=true ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-uiservices:
kafbat-ui:
container_name: kafbat-ui
image: ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui
ports:
- 8080:8080
environment:
DYNAMIC_CONFIG_ENABLED: true
volumes:
- ~/kui/config.yml:/etc/kafkaui/dynamic_config.yamlIn this article, we'll guide how to set up Kafbat-UI with role-based access control.
First of all, you'd need to set up authentication method(s). Refer to article for setup.
First of all, you have to decide if either:
You wish to store all roles in a separate config file
Or within a main config file
This is how you include one more file to start with a docker-compose example:
Alternatively, you can append the roles file contents to your main config file.
In the roles file we define roles, duh. Every role has access to defined clusters:
A role also has a list of subjects which are the entities we will use to assign roles to. They are provider-dependant, in general, they can be users, groups, or some other entities (github orgs, google domains, LDAP queries, etc.) In this example we define a role memelords that will contain all the users within the Google domain memelord.lol and, additionally, a GitHub user Haarolean. You can combine as many subjects as you want within a role.
The subject value is either a fixed string or a regular expression identifying a subject. To use regular expression, you must set regex: true. Regular expression works for any combination of provider and type. In this example, we define a role admins that will contain all the users with an oauth role ending with -ADMIN.
A list of supported providers and corresponding subject fetch mechanism:
oauth: user, role
oauth_google: user, domain
oauth_github: user, organization
More on identity providers in:
Find the more detailed examples in a full example file lower.
The next thing which is present in your roles file is, surprisingly, permissions. They consist of:
Resource Can be one of the: CLUSTERCONFIG, TOPIC, CONSUMER, SCHEMA, CONNECT, KSQL, ACL.
The resource value is either a fixed string or a regular expression identifying a resource. Value is not applicable to clusterconfig
Actions
A list of all the actions for the corresponding resources (please note neither resource nor action names are case-sensitive):
applicationconfig: view, edit
clusterconfig: view, edit
A complete file example:
A read-only setup:
An admin-group setup example:
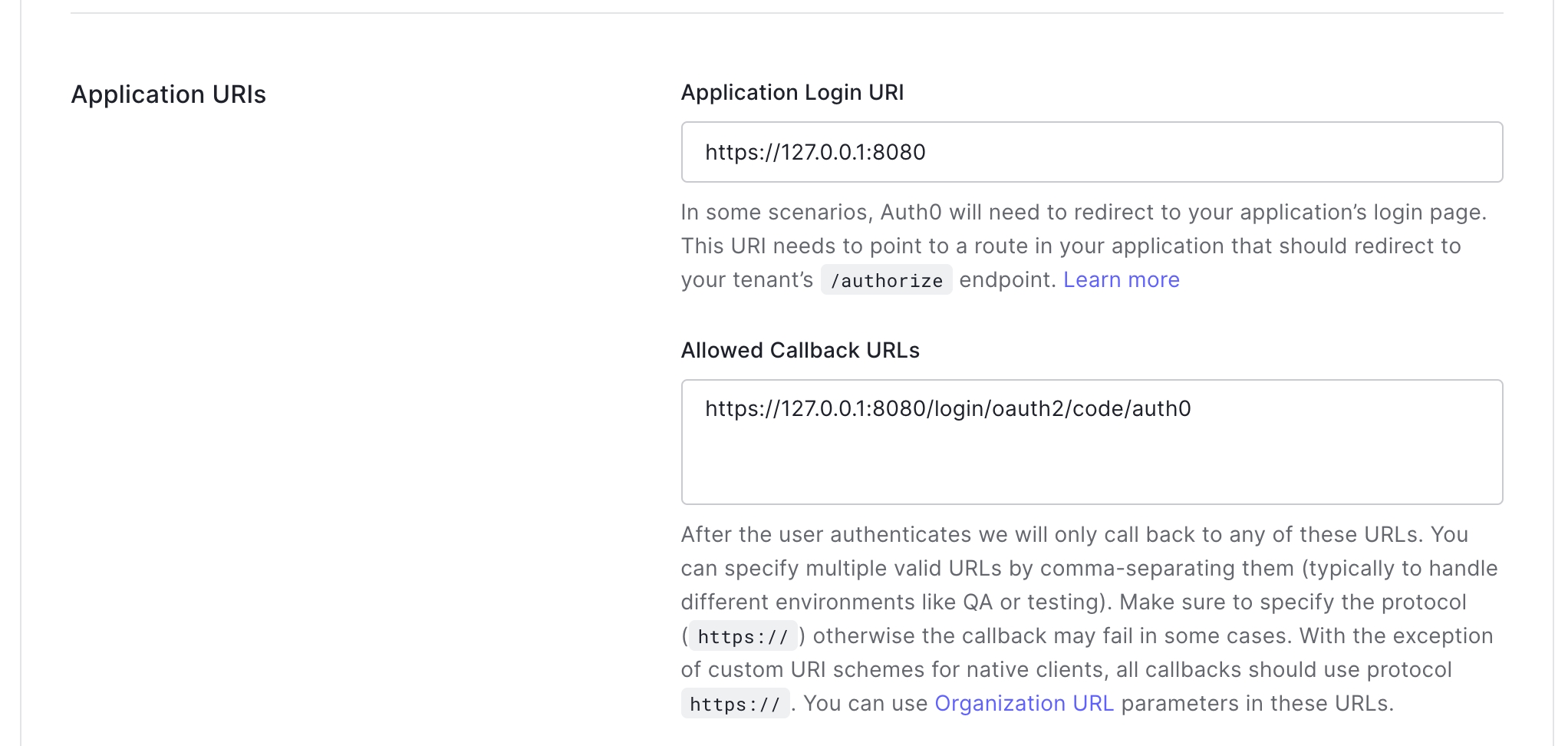
teamoauth_cognito: user, group
ldap: user, group
ldap_ad: user, group
ksqlActions It's a list of actions (the possible values depend on the resource, see the lists below) that will be applied to the certain permission. Also, note, there's a special action for any of the resources called "all", it will virtually grant all the actions within the corresponding resource. An example for enabling viewing and creating topics whose name start with "derp":
topic: view, create, edit, delete, messages_read, messages_produce, messages_delete, analysis_run, analysis_viewconsumer: view, delete, reset_offsets
schema: view, create, delete, edit, modify_global_compatibility
connect: view, edit, create, delete,operate, reset_offsets
ksql: execute
acl: view, edit
audit: view
client_quotas: view, edit
services:
kafbat-ui:
container_name: kafbat-ui
image: ghcr.io/kafbat/kafka-ui
environment:
KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: local
# other properties, omitted
SPRING_CONFIG_ADDITIONAL-LOCATION: /roles.yml
volumes:
- /tmp/roles.yml:/roles.ymlrbac:
roles:
- name: "memelords"
clusters:
- local
- dev
- staging
- prod - name: "memelords"
subjects:
- provider: oauth_google
type: domain
value: "memelord.lol"
- provider: oauth_github
type: user
value: "Haarolean"
- provider: oauth
type: role
value: "admin" - name: "admins"
subjects:
- provider: oauth
type: role
value: ".*-ADMIN"
regex: true permissions:
- resource: topic
value: "derp.*"
actions: [ VIEW, CREATE ]rbac:
roles:
- name: "memelords"
clusters:
- local
- dev
- staging
- prod
subjects:
- provider: oauth_google
type: domain
value: "memelord.lol"
- provider: oauth_google
type: user
value: "[email protected]"
- provider: oauth_github
type: organization
value: "memelords_org"
- provider: oauth_github
type: team
value: "memelords_org/memelords_team"
- provider: oauth_github
type: user
value: "memelord"
- provider: oauth_cognito
type: user
value: "username"
- provider: oauth_cognito
type: group
value: "memelords"
# AzureAD with OAUTH2
- provider: role
type: user
value: "[email protected]"
- provider: oauth
type: role
value: "admin"
- provider: ldap
type: user
value: "username"
- provider: ldap
type: group
value: "admin_staff"
- provider: ldap_ad
type: user
value: "username"
- provider: ldap_ad
type: group
value: "admin_staff"
permissions:
- resource: applicationconfig
# value not applicable for applicationconfig
actions: [ "view", "edit" ] # can be with or without quotes
- resource: clusterconfig
# value not applicable for clusterconfig
actions: [ "view", "edit" ]
- resource: topic
value: "ololo.*"
actions: # can be a multiline list
- VIEW # can be upper or lowercase
- CREATE
- EDIT
- DELETE
- MESSAGES_READ
- MESSAGES_PRODUCE
- MESSAGES_DELETE
- ANALYSIS_RUN
- ANALYSIS_VIEW
- resource: consumer
value: "\_confluent-ksql.*"
actions: [ VIEW, DELETE, RESET_OFFSETS ]
- resource: schema
value: "blah.*"
actions: [ VIEW, CREATE, DELETE, EDIT, MODIFY_GLOBAL_COMPATIBILITY ]
- resource: connect
value: "local"
actions: [ view, edit, create, delete, operate, reset_offsets ]
# connectors selector not implemented yet, use connects
# selector:
# connector:
# name: ".*"
# class: 'io.kafbat.connectorName'
- resource: ksql
# value not applicable for ksql
actions: [ execute ]
- resource: acl
# value not applicable for acl
actions: [ view, edit ]
rbac:
roles:
- name: "readonly"
clusters:
# FILL THIS
subjects:
# FILL THIS
permissions:
- resource: clusterconfig
actions: [ "view" ]
- resource: topic
value: ".*"
actions:
- VIEW
- MESSAGES_READ
- ANALYSIS_VIEW
- resource: consumer
value: ".*"
actions: [ view ]
- resource: schema
value: ".*"
actions: [ view ]
- resource: connect
value: ".*"
actions: [ view ]
- resource: acl
actions: [ view ]
rbac:
roles:
- name: "admins"
clusters:
# FILL THIS
subjects:
# FILL THIS
permissions:
- resource: applicationconfig
actions: all
- resource: clusterconfig
actions: all
- resource: topic
value: ".*"
actions: all
- resource: consumer
value: ".*"
actions: all
- resource: schema
value: ".*"
actions: all
- resource: connect
value: ".*"
actions: all
- resource: ksql
actions: all
- resource: acl
actions: [ view ]